Troubleshooting IEC 61850 GOOSE Communications: A Practical Guide
IEC 61850 GOOSE (Generic Object-Oriented Substation Event) messaging is a cornerstone of modern digital substations, enabling real-time peer-to-peer communication between Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). However, despite its robustness, GOOSE messaging can sometimes fail, leaving engineers scratching their heads. In this guide, we’ll explore the most common issues, discuss the importance of isolating problems methodically, and outline a structured troubleshooting approach.
Common Issues in GOOSE Communication
When GOOSE messages don’t work as expected, the root cause often falls into one of the following categories:
1. Configuration Mismatch
The publisher’s configuration has been updated, but the subscriber hasn’t been synchronized. The subscriber is listening for a different dataset or GOOSE Control Block than what the publisher is sending.
2. Inconsistent/Incompatible Configuration
The publisher sends a dataset that includes data objects (data structures), but the subscriber can only process data attributes. Data type mismatches cause the subscriber to reject the received message.
3. Network Communication Failures
Physical Connection Failures: Loose or disconnected cables, faulty ports, or damaged fiber links. VLAN Configuration Errors: Publisher and subscriber reside on different VLANs or VLAN tagging is misconfigured. MAC Filtering Errors: Switch settings blocking the transmission of multicast GOOSE messages.
4. Unexpected IED Behaviour or Failure
Equipment Failure: The publisher or subscriber IED has hardware malfunctions or software bugs. Configuration Failure: Incorrect settings, failure to process SCD file, or unintentional disabling of GOOSE messaging.
The Key to Success: Isolate and Tackle Problems Independently
To troubleshoot GOOSE communication effectively, you must isolate the problem by categorizing issues into network-related and configuration-related problems.
Network-Related Troubleshooting
Step 1: Verify Physical Connections
Ensure network switch links are active. Check if any ports are disabled or experiencing high error rates. Confirm that data transmission is occurring by using a network analyzer.
Step 2: Check If the Publisher is Sending GOOSE Messages
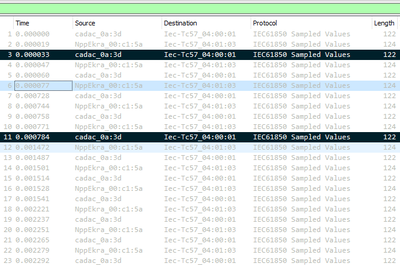
Verify that the GOOSE message is correctly configured in the IED. Use packet capture tools (such as Wireshark) to confirm that the GOOSE message is being sent. Connect to another switch port and check if the message is available.
Step 3: Confirm GOOSE Reception at the Subscriber’s Port
If possible, connect a laptop or test tool directly to the subscriber’s port and check if the message is arriving. If direct connection isn’t an option, enable port mirroring on the switch to inspect traffic reaching the subscriber. Keep in mind that different switches handle mirroring differently. Verify that the subscriber is capable of receiving other GOOSE messages (from different sources).
Step 4: Validate VLAN and MAC-Filtering Settings
If VLANs are used, ensure the GOOSE message VLAN ID matches the VLAN configuration on the switch. Verify that both the publisher’s and subscriber’s ports are members of the same VLAN. Check if MAC filtering or security settings are blocking the message.
Step 5: Debug Step-by-Step in Daisy-Chained Networks
If multiple switches are involved, test message availability at each switch in sequence. Start from the switch where the publisher is connected and verify the presence of the message at each step.
Configuration-Related Troubleshooting
Step 6: Verify Subscriber’s Configuration
Ensure that the subscriber is configured to receive the correct GOOSE Control Block. Check if the dataset structure matches what the subscriber expects (i.e., data objects vs. data attributes). Confirm that no errors exist in the configuration files that could prevent message parsing. If possible, send a simulated GOOSE message using an SCD file to verify that the subscriber can correctly interpret and process messages.
Step 7: Check for IED-Specific Issues
Ensure that firmware updates or configuration settings have not unintentionally disabled GOOSE reception. If possible, check the error logs of the subscriber for any rejection messages related to GOOSE processing.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting IEC 61850 GOOSE communication requires a structured approach, addressing both network and configuration aspects. By isolating potential issues and verifying each component independently, engineers can efficiently diagnose and resolve failures. Whether it’s a simple configuration mismatch or a more complex network issue, following these steps ensures a logical and effective resolution process.
💡 Have you encountered GOOSE communication issues in the field? What was the trickiest problem you had to solve? Join our digital substation community and let's discuss them!
last articles
Verification of SCD files for digital substations: requirements and practical experience
18 November 2021